Many patients with chronic medical problems make the mistake of eating too many carbohydrates and not enough protein in their diets. This can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, fatigue, arthritis, gastrointestinal problems, and mood disorders.
During this beginning phase of your treatment, you must first learn about the different food groups, and then start to change the relative amounts of proteins and carbohydrates.
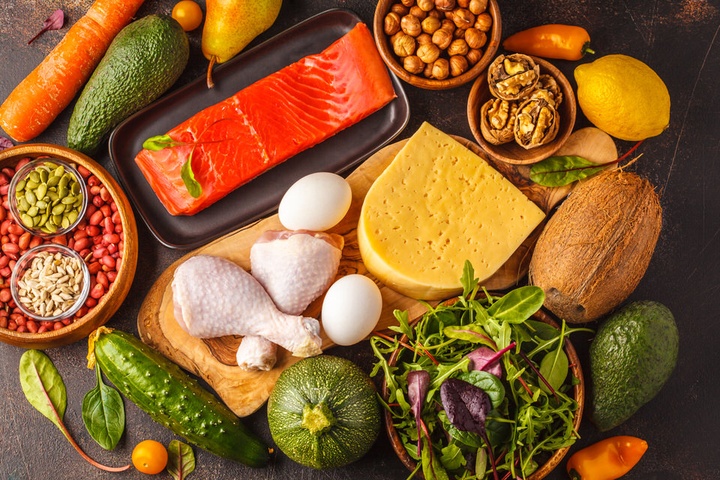
What is a carbohydrate? It is actually a very simple food, made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Carbohydrates are only used in the body as a source of energy. If you eat too many carbohydrates, your body will store this energy as fat. Examples of carbohydrates are; breads, pastas, rice, beans, cereals, fruits, fruit juices, potatoes, corn, beets, cakes, cookies, pretzels, potato chips, popcorn, soda, sugars, and anything that is naturally sweet.
What is a protein? Proteins are more complex than carbohydrates. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, they contain nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur.
In addition to being used as a fuel, proteins serve as the building blocks of your entire body. Proteins are used to build muscle, bone, connective tissue (ligaments, cartilage, joints), blood, enzymes, neurotransmitters and hormones.
Proteins in the form of meat, fish, poultry, eggs and cheese, have an additional nutritional advantage in that they are combined with very healthy and important fats. These fats are necessary for hormone production, to stabilize blood sugar levels and for keeping blood lipids (fats like cholesterol and triglycerides) stable.
At this point in your treatment, I want you to decrease the consumption of carbohydrates and increase the consumption of proteins in the form of meat, fish, poultry, eggs and cheese (however do not increase proteins in the form of nuts, nut butters, or soy).
Increasing green, leafy vegetables is also recommended as well as increasing the consumption of spring water.