The Work of Emanuel Revici MD
- Born in Romania in 1896, deceased in 1997
- A brilliant scientist and medical doctor
- Spent decades doing research in physiopathology
- Published his seminal book in 1961 describing a previously unknown homeostatic control mechanism
- Revici’s license to practice medicine was revoked in 1993
- Revici’s contributions have been marginalized in conventional medicine despite profound implications of his work

Anabolic – Catabolic Imbalances
- A common, but rarely recognized cause of chronic illness
- Also referred to as Anaerobic/Dysaerobic imbalance
- The Anaerobic imbalance is also known as the “Warburg Effect”- or anerobic glycolysis – also associated with “reductive stress”
- The Dysaerobic imbalance is associated with “oxidative stress”

Start your journey to true well-being:
Subscribe to our email list and receive valuable health tips, essential wellness recommendations, and our free guide, “13 Ways to Increase Your Healthspan,” delivered straight to your inbox. Join our community and take the first step towards a healthier tomorrow!
Balance Between Anabolic and Catabolic Tendencies is Vital for Health
- In a balanced state there are sufficient sterols and fatty acids to allow the cells to produce energy in an efficient manner
- Enough sterols to control oxidative stress
- Enough fatty acids to facilitate oxidative metabolism
- Appropriate membrane permeability
- Appropriate pH balance between intracellular and extracellular compartments
Anabolic/Catabolic Balance is Achieved Toward the Middle of the Curve
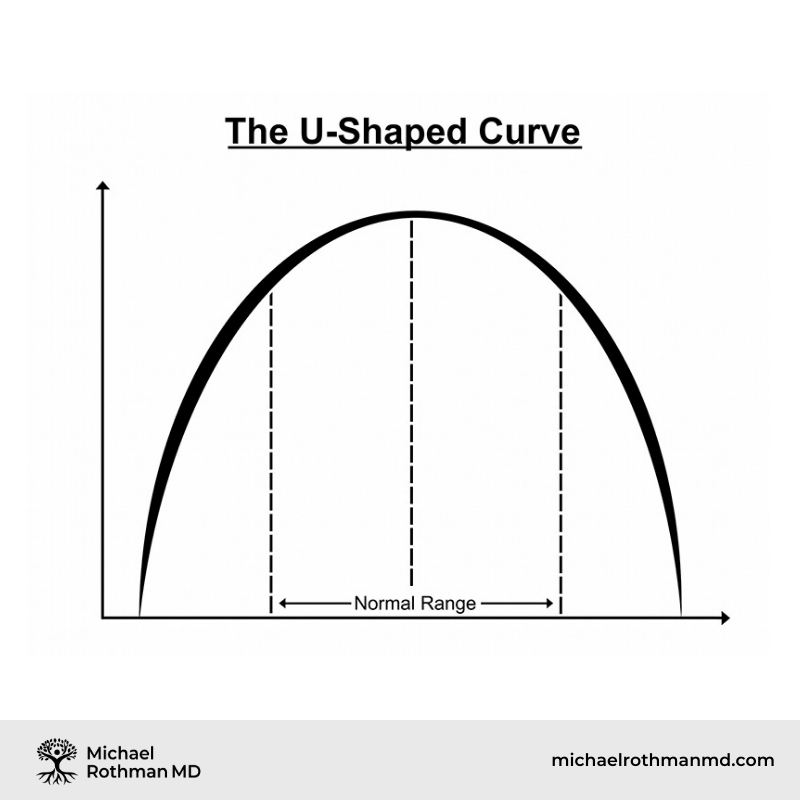
A Balance Between Fatty Acids and Sterols
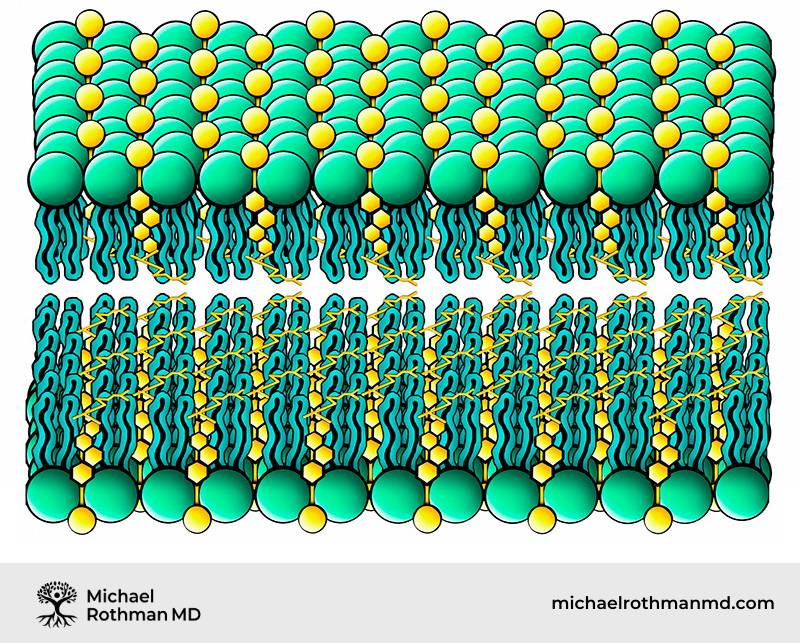
Anabolic (Anaerobic)
- Caused by excessive sterol activity within lipid bilayer of cell and mitochondrial membranes
- The relative lack of free fatty acids available to bond with oxygen leads to an anaerobic metabolic state
- This anaerobic state leads to increased growth of connective tissue and dedifferentiated growth
- Decreased membrane permeability
- Excess tissue acidity and excess systemic alkalinity
Too Many Sterols
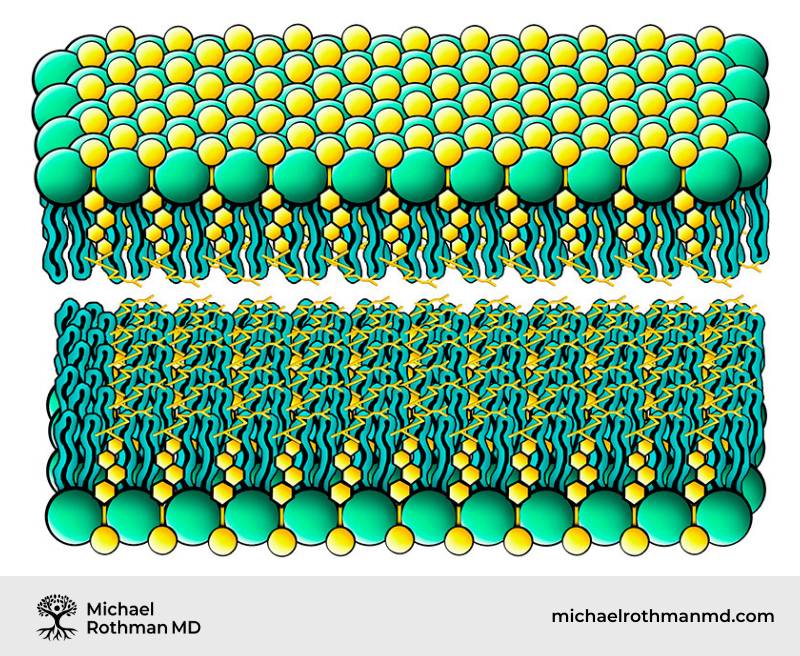
Anaerobic Patterns
- Common Symptoms -constipation, sleepy fatigue, polyuria, depression, burning pain (tissue acidity), adverse response to prednisone
- Lab Findings – may have -low CRP, low serum cholesterol, high estrogen, high progesterone, high cortisol, increased symptoms during mid-luteal phase of cycle
- Metabolic Tests – low urine SG < 15, high urine pH > 6.2, low saliva pH < 6.7, slow absorption of skin wheel
- Benefit from relatively low cholesterol foods
- Benefit from sulfur products
Ready to Take Control of Your Health?
If you’re ready to prioritize your health and are seeking effective, metabolically directed treatments, contact us online or call (732) 268-7663 for a consultation with Dr. Rothman.
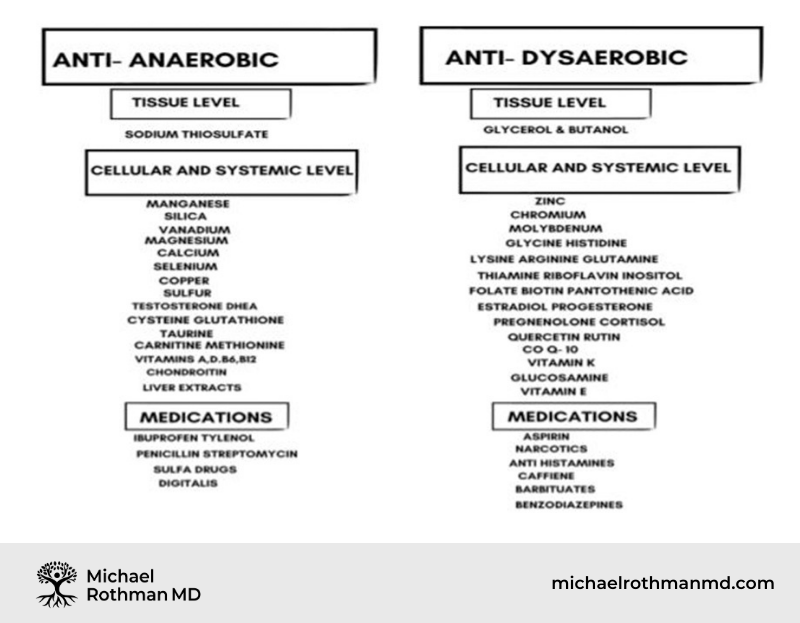
Anaerobic Overview
- Anaerobic (lack of oxygen- also known as anaerobic glycoysis = Warburg Effect) – Lactic acid is a product of anaerobic metabolism
- Treatment – Relatively low cholesterol diet, Oxytonic (sodium thiosulfate), Oxygenic A ,Taurine.
Catabolic (Dysaerobic)
- Caused by excessive fatty acid activity within lipid bilayer of cell and mitochondrial membranes
- The relative lack of sterols available to bind to fatty acids exposes these fatty acids to excessive oxidative stress
- This dysaerobic state leads to decreased growth of connective tissue and degeneration
- Increased membrane permeability
- Excess tissue alkalinity and excess systemic acidity
Too Many Fatty Acids, Not Enough Sterols
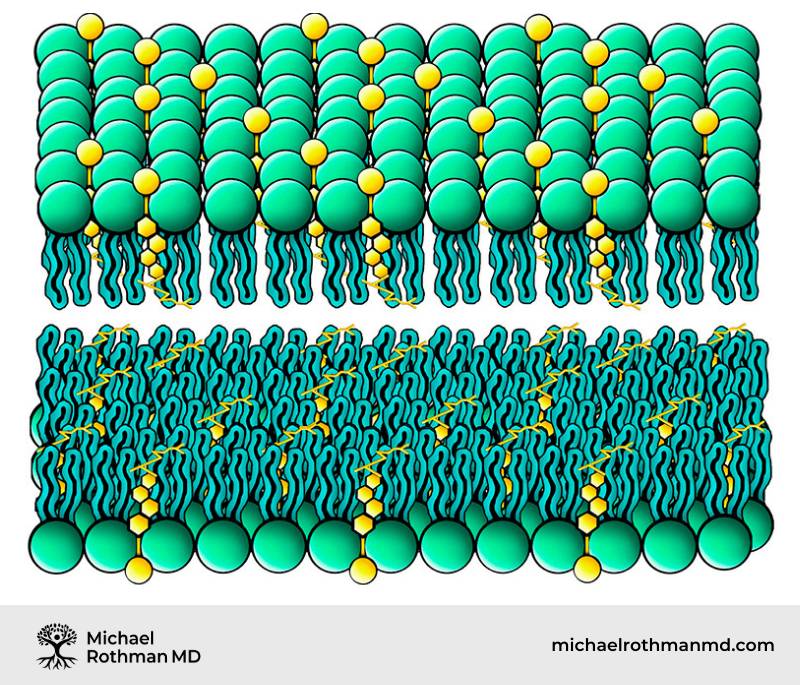
Dysaerobic Patterns
- Common Symptoms – diarrhea, burnt out fatigue, insomnia, anxiety oliguria, sharp pain (tissue alkalinity) responds well to prednisone
- Lab Findings – may have -high CRP, high serum cholesterol, low estrogen, low progesterone, low cortisol, increased symptoms during menses
- Metabolic Tests – high urine SG > 15, low urine pH < 6.1, high saliva pH > 6.7, rapid absorption of skin wheel
- Benefit from relatively high cholesterol foods
- Reacts poorly to sulfur products – dysaerobic symptoms
Dysaerobic Overview
- Dysaerobic (dysfunctional use of oxygen) = excess FA Deficient in sterols = chloride pulled into FA leaving behind carbonates that cause tissue alkalinity- Saliva alkaline Treatment – High Cholesterol Diet, Oxygenic D+(glycerol and butanol), Oxygenic D, Glycine
Therapeutic Agents Effects on Imbalances